Diabetes is dangerous because high blood sugar isn't usually something you can feel. Many people have no outward type 2 diabetes symptoms at all and can go years without being diagnosed.
That's why it's important to be aware of the type 2 diabetes symptoms and risk factors for diabetes (see below). Get screened by a physician if you have the following type 2 diabetes symptoms:
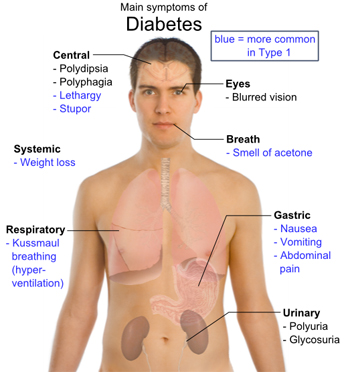
| Being unusually thirsty
Having to urinate often
Feeling hungry all the time
Losing weight (without trying)
Having blurry vision
Feeling very tired
Frequent infections
Cuts and sores that heal slowly
|
 |
As many as half of all Americans with diabetes are undiagnosed. Without proper diagnosis, other complications caused by high blood sugar can slowly develop.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
Experts agree that there are certain lifestyle and genetic risk factors for type 2 diabetes. People who are the greatest risk of developing diabetes include those who:
- Are age 45 or older
- Are overweight
- Have a family member (such as a parent, brother or sister) with diabetes
- Are not physically active
- Are African American, Latino, Native American, Asian American or Pacific Islander
- Have had high blood sugar levels in the past
- Have had a baby weighing more than 9 pounds (4.1 kg) or have had gestational diabetes
- Have high blood pressure (greater than 140/90 mmHg in adults)
- Have low ("good") cholesterol (less than or equal to 35 mg/dL)
- Have a high level of fats (triglycerides) in the blood (greater than or equal to 250 mg/dL)
- Have a history of vascular disease
- Have PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome)
If you are over age 45, talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for diabetes, especially if you are overweight or have family members with the condition. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that people over age 45 be retested every 3 years.
Regardless of your age, if you are overweight and have one or more of the other risk factors listed above, the ADA suggests that you be tested for diabetes now. |